How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, innovative surveying, and exciting recreational pursuits. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced maneuvering techniques and post-flight maintenance. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, flight planning strategies, and legal considerations, empowering you to confidently take to the skies.
From understanding the fundamental controls of your drone – throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll – to mastering advanced maneuvers and capturing breathtaking aerial footage, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to become a proficient drone pilot. We’ll also delve into the crucial aspects of legal compliance and responsible drone operation, ensuring your flights are both safe and within the bounds of the law.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. Failing to perform these checks can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, or even injury. This section details the necessary steps and safety considerations.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, a thorough inspection of the drone and its components is paramount. This involves visually checking for any physical damage, ensuring all parts are securely attached, and verifying the functionality of key systems.
| Check Item | Pass/Fail | Notes | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Minimum 20% recommended | Replace if below minimum | |
| GPS Signal Strength | At least 8 satellites | Relocate to area with better signal | |
| Propeller Condition | Check for cracks or damage | Replace damaged propellers | |
| Gimbal Function | Smooth movement, no unusual noises | Calibrate if necessary | |
| Camera Functionality | Check image/video feed | Adjust settings if needed | |
| Flight Controller Status | Firmware up-to-date, no error messages | Update firmware if needed |
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to local regulations and best practices is essential for responsible drone operation. This includes understanding airspace restrictions, maintaining visual line of sight, and respecting privacy concerns.
- Always obtain necessary permissions before flying in restricted areas.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Avoid flying near airports, stadiums, or other sensitive locations.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Never fly your drone under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding the basic controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective drone operation. This section covers the essential controls and flight modes, as well as a step-by-step guide for basic maneuvers.
Drone Controls
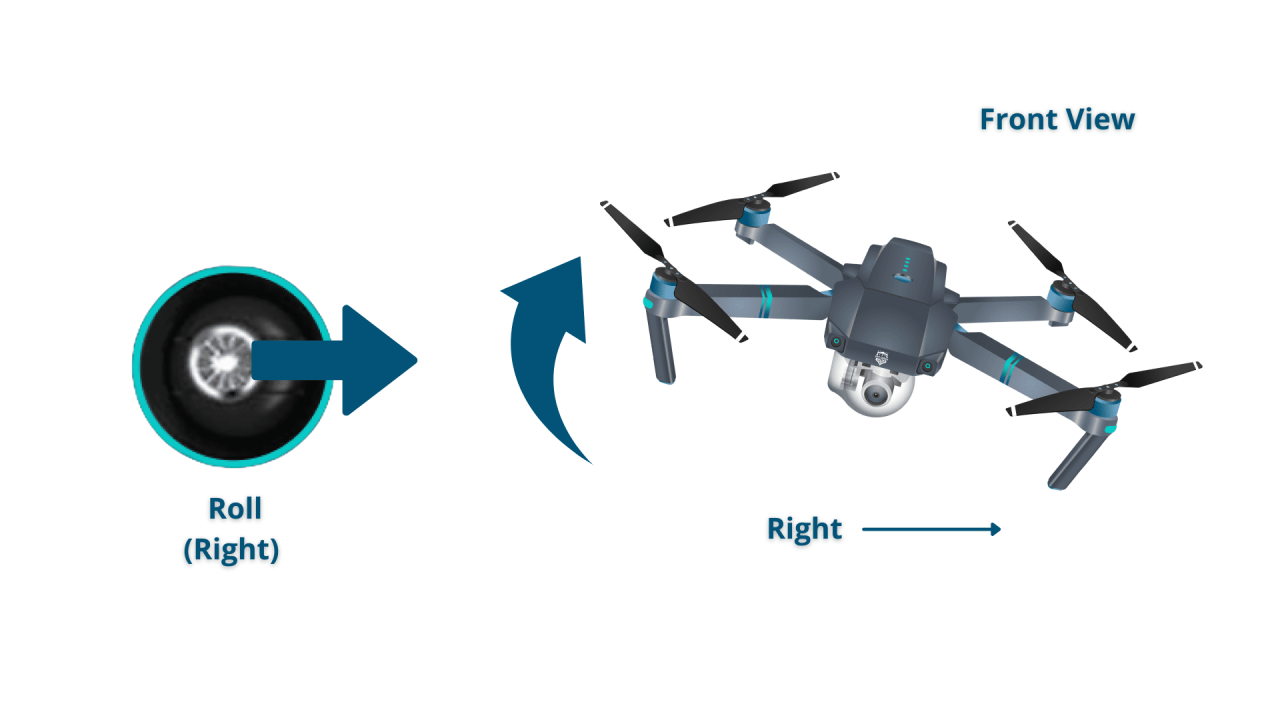
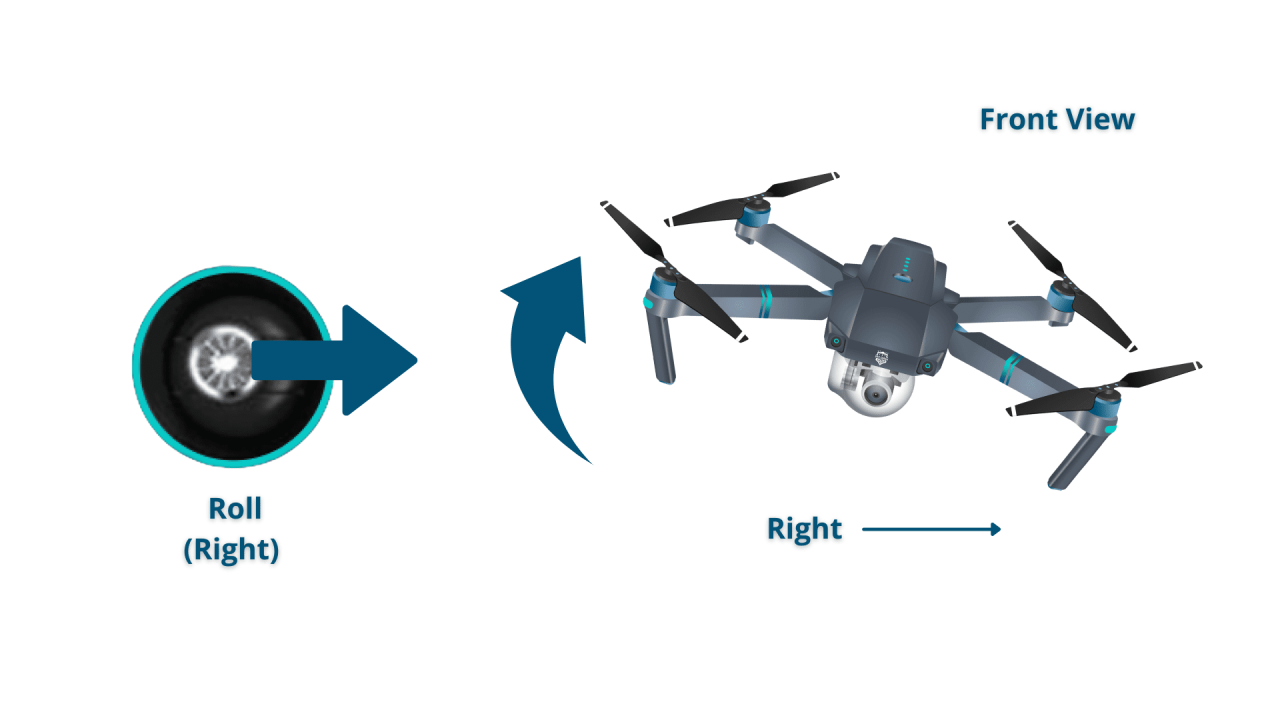
Most drones use a controller with sticks and buttons to control the drone’s movement. The primary controls are throttle (altitude), yaw (rotation), pitch (forward/backward tilt), and roll (left/right tilt).
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires understanding regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal considerations, consult this helpful resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Safe and responsible operation is paramount for enjoyable and legal drone use.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. GPS mode uses satellite signals for precise positioning, while Attitude mode relies on the drone’s internal sensors for stability. Sport mode often allows for faster and more agile maneuvers, but requires more skill.
- GPS Mode: Provides stable flight and precise hovering, ideal for beginners.
- Attitude Mode: Offers more agile control but requires more skill to maintain stability.
- Sport Mode (if available): Unlocks faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, demanding significant piloting skill.
Controller Types, How to operate a drone

Various controller types exist, each with advantages and disadvantages. Some offer more features, longer range, or ergonomic designs. The choice depends on individual needs and preferences.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires understanding regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and effective flight. Ultimately, responsible drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and consistent practice.
- Standard Controllers: Typically included with the drone, offer basic functionality.
- Advanced Controllers: May include features like customizable controls, longer range, and integrated screens.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
- Perform pre-flight checks.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift off.
- Maintain a steady throttle for hovering.
- Slowly decrease the throttle to land gently.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Flight Planning and Maneuvering Techniques
Proper flight planning and smooth maneuvering techniques are essential for safe and efficient drone flights. This section covers key considerations and techniques for controlled drone operation.
Flight Planning

Before each flight, careful planning is necessary. This includes checking weather conditions, identifying potential hazards, and understanding airspace restrictions. Battery life must also be considered to ensure sufficient power for the flight and a safe return.
Maneuvering Techniques
Smooth and controlled maneuvers require practice and precision. This involves mastering the use of the control sticks to execute precise turns, directional changes, and altitude adjustments.
| Maneuver | Control Input | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Flight | Push the right stick forward | Moves the drone forward in the direction it is facing |
| Backward Flight | Pull the right stick backward | Moves the drone backward |
| Left Strafe | Push the left stick left | Moves the drone left, maintaining its orientation |
| Right Strafe | Push the left stick right | Moves the drone right |
| Yaw (Rotation) | Rotate the left stick | Rotates the drone left or right |
| Ascent | Push the right stick upward | Increases the drone’s altitude |
| Descent | Pull the right stick downward | Decreases the drone’s altitude |
Common Flight Errors and Solutions
Understanding common flight errors and their solutions is vital for preventing accidents and improving piloting skills. Common errors include loss of GPS signal, low battery warnings, and uncontrolled movements.
- Loss of GPS signal: Relocate to an area with better signal reception.
- Low battery warning: Land immediately and replace the battery.
- Uncontrolled movements: Recalibrate the drone’s sensors and check for any mechanical issues.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality photos and videos with a drone requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section explores optimizing camera settings and achieving cinematic footage.
Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for optimal image quality. These settings affect brightness, sharpness, and motion blur. Experimentation is key to finding the best settings for different lighting conditions.
Camera Angles and Shot Composition
Different camera angles and shot compositions create varied visual effects. Experimenting with angles such as high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and dynamic tracking shots can greatly enhance the visual storytelling.
Capturing Smooth Cinematic Videos
Smooth, cinematic drone videos are achieved through careful planning, smooth maneuvers, and post-production editing. Using smooth, deliberate movements and avoiding sudden changes in direction or altitude contributes to a professional look.
Optimal Camera Angles
Visualizing optimal camera angles for different shot types is essential for effective storytelling. An establishing shot, for example, might utilize a high-angle, wide shot to showcase the environment. A close-up, conversely, would require a much closer and more detailed perspective.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of your drone. This section Artikels the steps involved in caring for your drone after each flight.
Storing and Maintaining the Drone
After each flight, store the drone in a clean, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Properly storing the battery is crucial to prevent damage and ensure its longevity. Regularly inspect the drone for any signs of damage or wear and tear.
Cleaning and Inspecting the Drone
Gently clean the drone body and propellers after each flight to remove dirt, dust, and debris. Inspect all components for any signs of damage, such as cracks, bends, or loose parts. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of your drone. This includes cleaning, inspecting, and replacing worn-out parts as needed. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance is crucial.
Essential Post-Flight Steps
- Power off the drone and controller.
- Remove the battery and store it properly.
- Clean the drone and propellers.
- Inspect for any damage.
- Store the drone in a safe and dry location.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for responsible and legal drone operation. This section covers the importance of regulatory compliance and how to check airspace restrictions.
Understanding and Adhering to Local Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and are constantly evolving. It’s essential to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before operating a drone. These regulations often cover areas such as flight altitude, proximity to airports, and required registrations.
Situations Where Drone Operation Might Be Restricted
Drone operation may be restricted or prohibited in various situations, including near airports, sensitive infrastructure (power plants, military bases), and during emergencies. Flying over crowds or private property without permission is also often illegal.
Resources for Finding Local Drone Laws
Many government agencies and organizations provide resources to help drone pilots understand and comply with local regulations. These resources often include online databases, publications, and contact information for relevant authorities.
Checking Airspace Restrictions
Before each flight, it is crucial to check for airspace restrictions using online tools provided by aviation authorities. These tools allow pilots to identify restricted areas and plan their flights accordingly. The process usually involves entering the flight location and date, and the tool will display any airspace restrictions in that area.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common drone problems, providing troubleshooting steps and preventative measures. Familiarizing yourself with these issues can save time and prevent costly repairs.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Several issues can arise during drone operation. Understanding potential causes and solutions is essential for effective troubleshooting.
| Problem | Potential Causes | Troubleshooting Steps | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | Replace battery, reduce flight time | Regularly charge battery, optimize flight settings |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructed signal, interference | Relocate to open area, recalibrate GPS | Fly in open areas, avoid interference sources |
| Motor Malfunction | Mechanical failure, loose connection | Inspect motors, check connections | Regular maintenance, avoid crashes |
| Gimbal Malfunction | Mechanical failure, software issue | Check for physical damage, recalibrate gimbal | Careful handling, regular maintenance |
| Unresponsive Controls | Low battery, controller interference | Check battery levels, move away from interference | Maintain sufficient battery power, avoid interference sources |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. By diligently following the pre-flight checks, understanding the controls, planning your flights meticulously, and adhering to safety regulations, you can unlock the incredible potential of drone technology. Remember, responsible drone piloting not only ensures your safety but also protects the airspace and the environment.
Soar safely and responsibly, and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that await you!
FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good flight time and easy-to-understand controls.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, execute a safe emergency landing procedure.
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store your drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, at around 50% charge when not in use for extended periods.